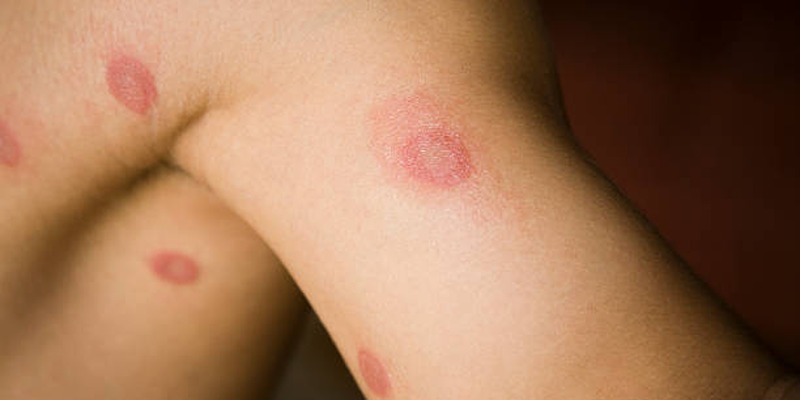
Ringworm is not caused by any worm but is a fungal infection that affects the skin, nails and the scalp. Tinea, is commonly referred to as ringworm even though it is not a worm, it is a circular, red rash that is usually itchy with a less swollen central area. Since the illness is easily transmitted, its prevention necessitates extensive awareness on how it can be contracted from humans, animals or objects. Ringworm is usually no big deal and can be treated simply with over the counter antifungal creams but if the skin condition is bad or becomes chronic then the doctor may prescribe other medications.
What is Ringworm?
Ringworm is a highly contagious skin infection that causes a red, ring-shaped rash with a clearer center, giving it its distinctive appearance. This infection can affect various parts of the body, including the scalp, feet, groin, and nails. The medical terminology for ringworm changes depending on the area it impacts:
- Tinea corporis: Ringworm on the body.
- Tinea capitis: Ringworm affecting the scalp.
- Tinea pedis: Commonly known as athlete's foot, it targets the feet.
- Tinea cruris: Often referred to as jock itch, it infects the groin area.
- Tinea unguium: Also called onychomycosis, it affects the nails.
Symptoms of Ringworm:
The signs may vary slightly, there are characteristic features to watch for. Below is an overview of the common symptoms based on location:
1. Skin Symptoms
- Red, scaly, or itchy patches that can develop anywhere on the body, often growing gradually over time.
- Raised, ring-shaped edges with a clearer center, giving the condition its distinctive "ring" appearance.
- In severe cases, blisters or oozing areas may form, signaling irritation or worsening infection.
2. Scalp Symptoms
- Bald patches caused by hair loss in affected areas, often mistaken for other scalp conditions.
- Scaly, crusty, or inflamed regions on the scalp, sometimes tender to the touch.
- Persistent itchiness that can lead to scratching, increasing the risk of secondary bacterial infections.
3. Nail Symptoms
- Nails that become thick, brittle, and discolored—shades of yellow, white, or brown are common.
- Over time, the infected nails may crumble or partially detach from the nail bed, potentially causing pain or discomfort.
- Nail infections are often more stubborn and challenging to treat compared to skin infections.
4. Foot Symptoms (Athlete's Foot)
- Cracked, dry, or peeling skin, particularly between the toes, creating a favorable environment for fungal growth.
- Itching or burning sensations, which may intensify after removing shoes or socks.
- Advanced cases might involve redness, swelling, or small blisters.
5. Groin Symptoms (Jock Itch)
- A red, itchy rash in the groin area, typically affecting the inner thighs and skin folds.
- Flaking or peeling skin, which can cause discomfort during movement or when wearing tight clothing.
- If untreated, the rash may spread to the thighs, buttocks, or lower abdomen, with sweating often worsening the condition.
Causes of Ringworm:
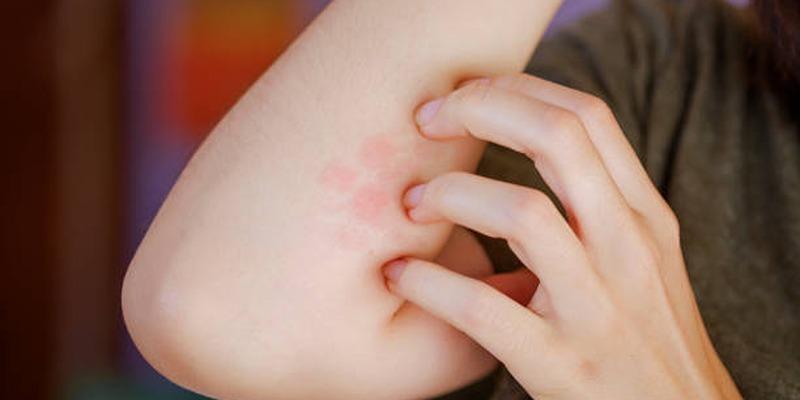

Ringworm is a common fungal infection caused by dermatophytes—a type of fungi that thrive in warm, humid environments. These fungi feed on keratin, a protein found in the skin, hair, and nails, making these areas particularly susceptible to infection. Highly contagious, ringworm spreads easily through various forms of contact. Below are the most common sources of transmission:
1. Human-to-Human Transmission
The most frequent way ringworm spreads is through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual. Even brief touch can transfer the fungi, especially if the skin has cuts, scrapes, or rashes that provide an entry point.
2. Animal-to-Human Transmission
Pets, such as cats, dogs, and even livestock, are common carriers of the fungi that cause ringworm. Infected animals may display symptoms like scaly skin or patches of missing fur, but they can also carry the infection without showing any signs.
3. Contact with Contaminated Objects
Sharing personal items contaminated by fungi is another common way ringworm spreads. Items such as towels, clothing, hairbrushes, combs, and bedding can harbor the fungi, making it easy to pass the infection to others.
4. Exposure to Contaminated Environments
Public spaces with warm, moist conditions—such as swimming pools, locker rooms, public showers, and gym mats—are ideal breeding grounds for fungi. Walking barefoot in these areas increases the risk of exposure, as fungi can survive on surfaces for extended periods.
How Is Ringworm Diagnosed?
Diagnosing ringworm usually begins with a physical examination of the affected area. Doctors may also use the following methods:
- Skin Scrapings: A small sample of skin is taken and examined under a microscope to detect fungal infections.
- Wood's Lamp Test: A specialized ultraviolet light helps identify fungal infections on the skin or scalp.
Effective Treatments for Ringworm:
Ringworm is a common fungal infection that can be effectively treated with the right care and medications. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and location of the infection.
1. Topical Antifungal Medications
- For mild skin infections, topical treatments like creams, lotions, or sprays are highly effective.
- Common options include Clotrimazole, Miconazole, and Terbinafine.
2. Oral Antifungal Medications
- For more severe or widespread infections, oral antifungal medications are often prescribed.
- Popular choices include Griseofulvin and Itraconazole.
3. Medicated Shampoos
- Scalp infections are best addressed with medicated shampoos.
- These shampoos help eliminate fungal spores and prevent the infection from spreading.
4. Treatments for Nail Infections
- Fungal nail infections, which are more resistant to treatment, may require specialized approaches like antifungal nail lacquers or oral medications for effective results.
Home Remedies and Preventive Strategies for Managing Ringworm:
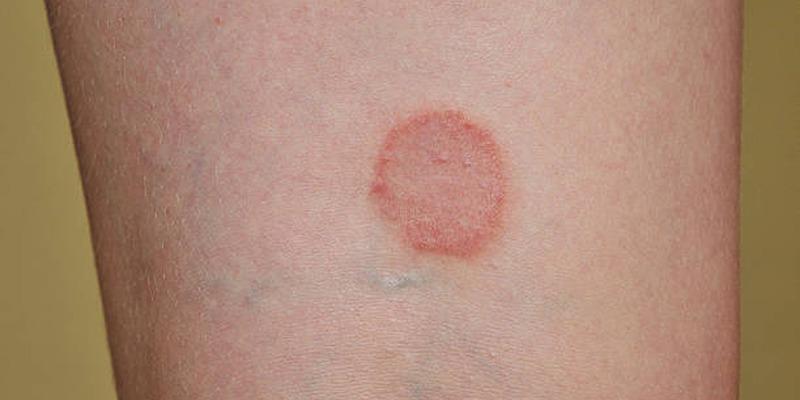
While medical treatment is crucial for addressing ringworm, integrating home remedies and preventive practices can support recovery and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Effective Home Remedies:
- Tea Tree Oil: Renowned for its antifungal properties, tea tree oil can be applied to the affected area after diluting it with a carrier oil to prevent skin irritation.
- Aloe Vera: Naturally soothing, aloe vera helps relieve itching and reduces irritation.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: A natural antifungal remedy, apple cider vinegar can be dabbed onto the affected area using a cotton ball for added relief.
Prevention Measures:
- Prioritize Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently and ensure your skin remains clean and dry to minimize fungal growth.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Refrain from sharing towels, combs, clothing, or other personal belongings to prevent the spread of infection.
- Address Pet Infections: If your pet displays signs of a fungal infection, consult a veterinarian promptly to prevent transmission.
Conclusion:
Ringworm is a common yet manageable condition when diagnosed and treated promptly. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help prevent its spread and ensure effective management. Maintaining good hygiene, treating infections early, and avoiding potential sources of contamination are key to keeping ringworm at bay.